Graduate school can be expensive, but scholarships can make it more affordable. Scholarships are a great way for students to reduce the financial burden of tuition fees, books, and living expenses. There are two primary types of scholarships that grad students often encounter: need-based and merit-based. While both aim to support students, they have different eligibility requirements and application processes. This article will explore the key differences between need-based and merit-based scholarships, helping graduate students decide which type of scholarship may be the best fit for their needs.
What Are Need-Based Scholarships?
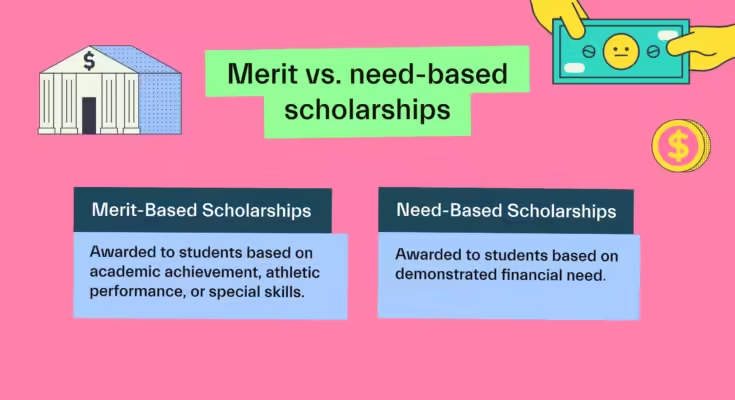
Need-based scholarships are awarded based on the student’s financial situation. These scholarships are designed to help students who may not have the financial resources to attend graduate school. The amount awarded depends on the financial need determined by the student’s family income, savings, and other financial factors.
- Eligibility: To qualify for need-based scholarships, students typically need to demonstrate their financial need through documentation such as tax returns, bank statements, and financial aid forms (like the FAFSA in the U.S.).
- Examples: Some universities offer need-based scholarships that are automatically considered when a student applies for financial aid, while private organizations may have specific need-based awards based on income thresholds.
- Benefits: The primary benefit of need-based scholarships is that they help level the playing field for students who may not have the financial means to pursue higher education. These scholarships can cover partial or full tuition and reduce the amount students need to borrow.
What Are Merit-Based Scholarships?
Merit-based scholarships are awarded to students based on their academic, professional, or extracurricular achievements rather than financial need. These scholarships recognize students for their hard work, talent, and dedication in their field of study or outside pursuits.
- Eligibility: To qualify for merit-based scholarships, students must typically meet certain academic or performance standards. This might include maintaining a high GPA, achieving top scores on standardized tests (such as the GRE or LSAT), or demonstrating excellence in areas like leadership, volunteer work, or specific talents like athletics or the arts.
- Examples: Some universities provide merit-based scholarships for students who have outstanding academic records. Private organizations and professional societies may also offer scholarships for students pursuing specific degrees, such as law or engineering, based on academic performance or other relevant achievements.
- Benefits: Merit-based scholarships reward students for their hard work and can also serve as a recognition of their potential. They offer an opportunity for high-achieving students to receive financial support without the need to demonstrate financial hardship.
Key Differences Between Need-Based and Merit-Based Scholarships
While both types of scholarships help reduce the cost of education, they differ in several key ways:
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Need-Based: Based on financial need. Eligibility depends on your family’s income and other financial factors.
- Merit-Based: Based on academic or extracurricular achievements. Eligibility depends on your academic performance, test scores, or special talents.
- Application Process:
- Need-Based: Requires financial documents such as the FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid) or tax returns to prove financial need.
- Merit-Based: Typically requires academic transcripts, standardized test scores, personal statements, and letters of recommendation.
- Award Amounts:
- Need-Based: The scholarship amount varies depending on your demonstrated financial need and the school’s resources.
- Merit-Based: The amount is often determined by the level of achievement and may be fixed (e.g., a $5,000 scholarship for top performers).
- Renewability:
- Need-Based: These scholarships may need to be renewed each year by demonstrating continued financial need.
- Merit-Based: Some merit-based scholarships are renewable as long as the student maintains certain academic standards (e.g., maintaining a GPA above a certain threshold).
- Impact on Financial Planning:
- Need-Based: These scholarships reduce the amount you need to borrow or work to pay for school, helping you attend if financial resources are limited.
- Merit-Based: These scholarships reward your achievements and provide financial assistance without regard to your financial situation, which may allow you to reduce reliance on loans or take fewer student loans.
Which Scholarship Is Right for You?
When deciding whether to pursue need-based or merit-based scholarships, it’s important to consider your personal circumstances:
- Need-Based Scholarships: If you come from a background where finances are a concern, need-based scholarships may be the best fit. They can significantly reduce the financial burden of grad school and allow you to focus on your studies without worrying about funding.
- Merit-Based Scholarships: If you have strong academic records or excel in extracurricular activities, merit-based scholarships are worth exploring. These scholarships reward your past achievements and can help ease the financial pressure of tuition.
- Combining Both: Many students are eligible for both types of scholarships. Combining need-based and merit-based awards can provide significant financial support and reduce the amount of debt you may incur during your graduate studies.
Additional Scholarship Resources for Grad Students
In addition to need-based and merit-based scholarships, there are other funding opportunities for graduate students:
- University Scholarships: Many universities offer internal scholarships, often with both need-based and merit-based options for incoming and current grad students.
- Private Scholarships: Numerous organizations, corporations, and foundations offer scholarships tailored to specific fields of study or demographics.
- Government Scholarships: Government programs, such as federal aid or specific programs for international students, can provide additional funding.
Tips for finding and applying for scholarships:
- Research scholarship opportunities early.
- Meet all deadlines and prepare thorough applications.
- Tailor your applications to match the scholarship’s specific criteria.
Conclusion
When considering scholarships for graduate school, understanding the differences between need-based and merit-based scholarships is crucial. Need-based scholarships can provide financial relief for students facing financial challenges, while merit-based scholarships reward academic excellence and achievements. Depending on your situation, you may find that applying for both types of scholarships can maximize your opportunities for funding. Whatever route you take, remember that scholarships are an excellent way to support your graduate education and reduce the need for student loans.



Some times its a pain in the ass to read what people wrote but this site is rattling user friendly! .
Wohh precisely what I was searching for, thankyou for putting up.